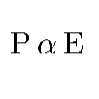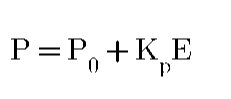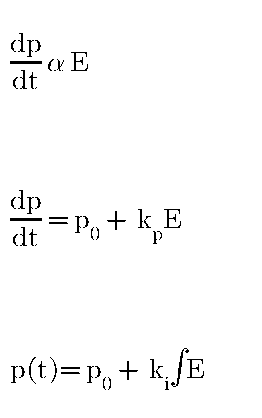PID Controlling mode in automation is explained here in simple terms. Calculations pros and cons included here
Reduce Oscillatory behavior
This blog contains following topics
- PID Control mode
- P Control mode Drawbacks and calculations
- I Control mode Drawbacks and calculations
- D Control mode Drawbacks and calculations
- How to tuning P [Gain], I [Reset] D[Rate] controls?
- Video - PID Controller in hindi
- PI Control mode
- PD Control mode
Interview Questions from this blog
- What is full form of PID Controlling?
- What is Rate control, Reset control and Gain in Controller?
- How to tune PID Controller?
- what is Zeigler Nichols method?
- How PID Controller works?
- What is mathematical expression of P I D Control system?
- What is error in controller?
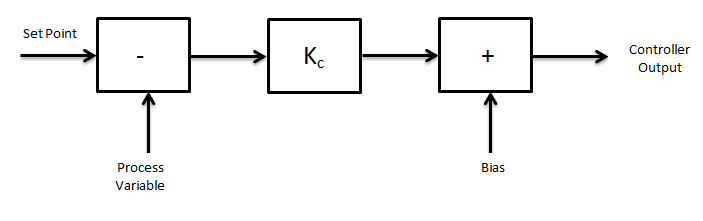
DCS controlling has combination of three modes
P - Proportional control mode
I - Integral control mode
D - Derivative control mode
Let we see basics of this modes
P - Proportional control mode (Gain control)
Proportional control mode is basic continuous control mode.
Here Controller output (P) is Proportional to the error (E)
P = Controller output
This is Set point or required field value which is given by DCS Person
E = Error Value
We can simply say difference between Set point and actual field value.
P0 = Controller output at zero error
Kp = Proportional gain constant
Controller value is equal to error[E] with constant gain[Kp] with output at zero error[P0].
 |
| P - Proportional control mode (Gain control) |
If Process value [Controller output, P] is equal to set point [ Error, E] then controller value will be zero. Steady state process is not possible so it run smoothly with steady error.
Properties of Proportional mode
- It is Characterized by a continuous linear relationship between input value and output value
- Exhibit offset (Offset means movement from its position example - Car wheel offset is 4 inch means wheel is moving up to 4 inch from his centre with help of Jumper)
- Lower stability
I - Integral Control Mode (Reset mode)
In Integral control mode Controller output value is proportional to Error
- P controller exist offset between Process value and set point so I – Integral control mode use becomes useful. Integral control mode eliminates steady state error.
- Integral mode integrate error over a period of time till error reach zero to field controlling devices like Valves, motors, VFDs etc.
- When negative error takes place I mode decreases its output.
 |
| Integral control mode |
Properties of Integral mode
- Eliminates offset
- It shows oscillatory behavior
Oscillatory behavior = Predictable variation from center point like Current, Voltage
- Large stabilization
Stabilization = Close enough to its center
D - Derivative control mode ( Rate Control mode)
Controller output is proportional to the rate of change in error.
Integral control mode cannot predict upcoming behavior of
error. When set point is changed it reacts normal.
Derivative control mode solve this problem be resetting
whole system.
Above equation shows controller output depends on rate of
change of error with respect to time with multiplied by derivative constant [Kd]
with controller output zero. By resetting system it gives kick start for system
response.
It provides no output when error is zero
All has individual drawbacks
P - Exhibit offset, Low stability
I - Oscillatory behavior
D - No output at zero error
Due to this reason PID is utilities
PID - Proportional Integral Derivative Control mode.
It is combined mode of
P - Proportional Mode,
I - Integral mode,
D - Derivative mode
We can clearly see that PID consisting all three Proportional, Integral and Derivative control modes combined. This mode can control Pressure, Temperature, pH, Flow, Redox, Speed, etc.
We can clearly see that PID consisting all three Proportional, Integral and Derivative control modes combined. This mode can control Pressure, Temperature, pH, Flow, Redox, Speed, etc.