1. What is Definition of Distillation?
2. What is Unit operation & Unit process?
Unit Operation -
Unit Operation is defined as operation in which mass & concentration of component is changed from inlet to outlet with external sourcesExample - Distillation Drying, Evaporation, Drying, Mixing, Crystallization, Leaching, in all this mass and concentration of components are changed but no change in chemical
Unit Process -
3. What are types of valves?
1. Globe valve
2. Gate valve
3. Ball valve
4. Butterfly valve
5. Diaphragm valve
6. Plug valve
7. Needle valve
8. Angle valve
9. Pinch valve
10. Slide valve
11. Flush bottom valve
12. Solenoid valve
13. Control Valve
14. Flow regulating valve
15. Back pressure regulating valve
16. Y-type valve
17. Piston valve
18. Pressure regulating valve
19. Check valve
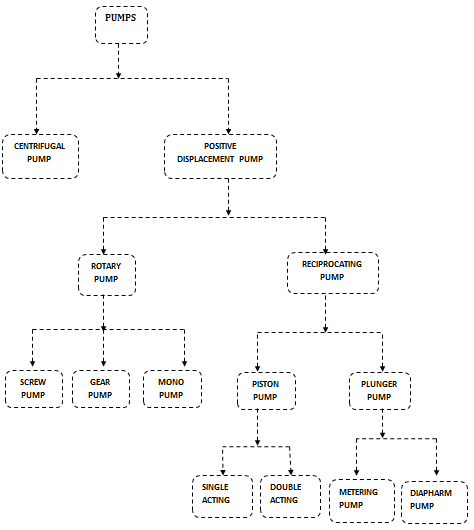
4. What are types of Pumps?
- Centrifugal Pump
- Positive Displacement Pump
- Rotary Pumps
- Reciprocating pump
- Screw pump
- Gear pump
- Mono pump
- Piston Pump
- Plunger pump
5. Types of Distillation
- Flash Distillation
- Batch Distillation
- Continuous Distillation
- Steam Distillation
- Extractive Distillation
- Azeotropic Distillation
6. What is LMTD ? Why we use LMTD to calculate overall heat transfer co efficient in shell & tube heat exchanger than arithmatic average?
U = Qt / ( At* LMTD )In heat exchanger hot fluid is losing heat and cold fluid is receiving heat this is not linear.
7. Which factors affecting heat transfer between fluids?
A. Types of fluid
Gas can transfer more heat comparison to liquid, and liquids can transfer more heat comparison to solid.
B. Types of material
Conductive material can easily transfer heat in comparison of resistivity material & Non metals.
C. Thickness of material
Equipment's with less thickness can easily transfer against higher thickness material.
D. Surface area
Heat transfer rate is directly proportional to surface material.
More active surface area more heat transfer.
Fourier's law
Q = - k A dt/dx
E. Liquid pressure
Liquids with high pressure can transfer more heat.
In high pressure molecules of fluid is more closer so vibration of heat can easily transfer atom to atom.
F. Turbulence of fluid
Fluid turbulence is directly proportional to turbulence of fluid.
Turbulence flow has high tendency of transfer heat than laminar flow.
This is the reason baffles are provided in heat exchanger.
G. Temperature difference between fluids.
High Temperature difference between two fluid can transfer more heat.
H. Thermal conductivity of equipment material of construction [MOC]
Each metal has unique conductivity to transfer heat. Copper has high thermal conductivity then Iron So, Copper can easily heat respect to Iron.
I. Velocity of fluids in heat exchanger
High velocity fluids prevent scaling and chocking in heat transfer equipment's so more heat transfer takes place in high velocity fluids.
J. Direction of Flow of fluids in exchange.
There are three flow patterns
Co current flow - Both fluids flowing in parallel stream
Split flow - Both fluids flow in right angle
Counter current flow - Both fluids are flowing in opposite direction
Heat transfer rate in fluids patterns
Co current flow < Split flow < Counter current flow
K. Amount of liquids
Heat exchanger gives more output when more amount of flow given.
8 State operational problems in distillation column
- Flooding
- Weeping/Dumping
- Entrainment
- Foaming
- Channeling
- Loading
- Flooding
8.1: What is flooding?
Depending on the degree of flooding, the maximum capacity of the column may be severely reduced.
8.2: What is weeping in distillation column?
8.3: What is Entrainment in distillation column?
8.4: What is Foaming in distillation column?
Whether foaming will occur depends primarily on physical properties of the liquid mixtures, but is sometimes due to tray designs and condition. Whatever the cause, separation efficiency is always reduced.
8.4: What is channeling in distillation column?
Down in the bed, the liquid tends to flow toward the wall.
8.5: What is loading in distillation column?
For example, through a section of fractionating trays, that comparison would be expressed as "percent of flood". Typical design is 80 to 85 percent of flood for a fractionator.
9: What is pervaporation?
10: What is reverse osmosis?
11. What is dew point ? Why it is important in instrument air?
Dew point is a temperature beyond this there is no vapour form of fluid exists in air. When air is condensed below its dew point then all moisture present in air will be condensate and air becomes completely dry.Instrument air used in costly instruments to operate. If we use moist air then it will harm to devices. This is the reason dew point is maintained in air around -40°C
12. What is difference between PFD and P&ID?
PFD - Process flow diagram.PFD is showing process flow diagram while P&ID is showing Valves, Pumps, Compressors and Instruments.
13. What is Floculation & Coagulation?
Floculation
- Floculation is physical operation.
- Any Fluid has solid waste particles or sludge then flocal agent convert into lump by making low to medium polymer chain and settle it down.
- Examples - METAC, Megnafloc
Coagulation
- Coagulation is chemical process.
- It is reacting with waste chemically with poly ionic materials
- Example - Aluminium sulphate, Aluminium Chloride, Hydrochloric acid, Alum,
14. What is difference between Bubble point and Boiling Point? What is Different between dew point & Freezing?
Definitions
Dew Point -
Boiling Point -
If we have binary fluid mixture and we are increasing temperature then Boiling point of less volatile component is change with respect to High volatile component.When Fluid mixture initial boiling is started then less volatile fluid start vaporizing is started and in more volatile liquid its vaporize later.
Dew point
Freezing point
Answer: The relative volatility is the ratio of the K values for two components. It is denoted by ‘α’
In distillation if relative volatility is high then it is easy to separate fluid mixture and few numbers of trays required but if relative volatility is near 1 then it’s difficult to distillate fluid mixture.
Relative volatility is reduced if column pressure is increased.
16. What is molecular sieve?
Molecular sieve means a solid micro porous alumina silicate with uniform pore geometry it is called as zeolite17. What is definition of Pervaporation?
- It is membrane separation technique for liquid-liquid separation technique.
- Permeate liquid is brought in contact to vacuum and extracted as vapour
18. What is RO – Reverse Osmosis?
- Solution is subjected to Membrane.
- Membrane allow to pass solvent from one portion to another
- This is method used to separate water.
19.How to use Gate Valve, Globe Valve & Ball valve?
- Gate Valve – Fully on or off condition.
- Globe Valve – Throttling purpose design.
- Ball valve – Quick On or off valve.
20. Why cyclone separator has tangential entry?
- When laden gas enters in cyclone it forms swirl.
- This swirls separate dust and light particles.
- If there is straight entry these swirls not form and separation doesn’t takes place.
- This is the reason why tangential entry is in Cyclone separator.
21. What is surging in compressors and how it can be prevented?
22. Difference between latent heat & sensible heat.
Latent heat
Sensible heat
23. What is crystallization? Give Name of crystallizers.
Crystallization
Name of crystallizers
- Vacuum crystallizer
- Agitated tank crystallizer
- Swenson-walker crystallizer
- Draft tube crystallizer
24. Why Earthing is provided in Solvent line?
25. What is ISO & kaizen?
ISO
ISO (International Organization for standardization) is an international standards- setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations.Kaizen
It is Japanese word that refers to activities that continuously improve all functions & involve all employees from the CEO to the assembly line workers.26. Write the name of strong acid and strong, Give examples of weak acid and weak base.
Strong Acid
Strong Base
NaOH - Sodium HydroxideKOH – Potassium Hydroxide
Ca(OH)2 - Calcium Hydroxide
Ba(OH)2 – Barium Hydroxide
Weak acid
Weak Base
NH3 (ammonia)C5H5N (pyridine)
NH4OH (ammonium hydroxide)
N(CH3)3 (Trimethyl ammonia)
27. Give Boiling Point of …
28. Define Write the name of one equipment use for measuring humidity.
Relative Humidity
It’s the ratio of the amount of moisture in the air to the maximum amount of moisture that could exist in the air at a specific temperature.Specific Humidity
It’s the ratio of the mass of moisture in the mixture to mass of moisture in air.Measuring equipment
HygrometerHydrometer
A hydrometer is an instrument that measure the specific gravity (relative density) of liquid.29. Differentiate compressors, fans and blowers?
- Fans, blowers and compressors are differentiated based on the method used to move the air and specific ratio (specific ratio= discharge pressure/suction pressure).
- As per the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) the compression ratio for fans is up to 1.11, blowers‑ 1.11 to 1.2 and for compressors above 1.2
30. What is dew point and why it is important in instrument air?
31. What is pervaporation?
What is definition of Pervaporation?
33. What is dew point and why it is important in instrument air?
- The Dew Point is the temperature at which water vapor starts to condense out of the air (the temperature at which air becomes completely saturated). Above this temperature the moisture will stay in the air.
- Electronic instruments uses instrument air received from instrument compressors must be free of any moisture. Small amount of moisture may condensate & it may harmful to instruments So the instrument air should be free of moisture. This is ensured by keeping the dew point below 400 C or below.
34. What are the color codes for cylinders? Colour codes of Industrial cylinders?
Colour coding helps identify gases quickly, avoid mistakes, and maintain strong industrial safety.
What are cylinder colour codes?
It is a standard system of painting gas cylinders in specific colours.
Each colour helps identify the type of gas and level of hazard.
Used in industries to avoid mix-ups, accidents and wrong gas connections.
Based on standards such as ISO / BS EN / country safety codes (may vary slightly by region).
Why are they important?
Safety — prevents wrong gas usage (oxygen vs nitrogen etc.)
Accident prevention — reduces fire, explosion and asphyxiation risks
Fast identification — even from a distance in emergencies
Compliance — meets statutory safety requirements
Easy maintenance & handling
Common industrial cylinder colour meanings
Oxygen — Black body with White shoulder
Nitrogen — Black body with Grey shoulder
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) — Grey body with Black shoulder
Argon — Dark Green or Blue-Green shoulder
Acetylene — Maroon
Hydrogen — Red shoulder
Compressed air — Light Grey body
Chlorine — Yellow shoulder
Helium — Brown shoulder
LPG / Propane — Red or Orange body
(Note: Exact shade/placement can differ by country or supplier — always verify plant standards.)
35. Please give a comparison between orifice meter and venturi meter Orifice meter
Venturi meter
1. The orifice plate can easily be changed to accommodate widely different flow rates, whereas the throat diameter of a venturi is fixed, so that its range of flow rates is circumscribed by the practical limits of Dp.
2. The orifice meter has a large permanent loss of pressure because of the presence of eddies on the downstream side of the orifice plate; the shape of the venturi meter prevents the formation of these eddies and greatly reduces the permanent loss.
3. The orifice is cheap and easy to install. The venturi meter is expensive, as it must be carefully proportioned and fabricated. Homemade orifice is often entirely satisfactory, whereas a venturi meter is practically always purchased from an instrument dealer.
4. On the other hand, the head lost in the orifice for the same conditions as in the venturi is many times greater.
The power lost is proportionally greater, and, when an orifice is inserted in a line carrying fluid continuously over long periods of time, the cost of the power may be out of all proportion to the saving in first cost.
Orifices are therefore best used for testing purposes or other cases where the power lost is not a factor, as in steam lines.
5. However, in spite of considerations of power loss, orifices are widely used, partly because of their greater flexibility, because installing a new orifice plate with a different opening is a simpler mater.
The venturi meter cannot be so altered. Venturi meters are used only for permanent installations.
6. It should be noted that for a given pipe diameter and a given diameter of orifice opening or venturi throat, the reading of the venturimeter for a given velocity is to the reading of the orifice as (0.61/0.98)2, or 1:2.58.(i.e. orifice meter will show higher manometer reading for a given velocity than venturi meter).
36. Definitions: Partial pressure, Vapour pressure, Diffusivity
Partial pressure
The pressure of component gas that is present in mixture of gases.
The total pressure of mixture of gases = partial pressure of the component gas which are present in mixture of gas.
Vapour pressure
The pressure exhibited by vapour on liquid or solid surface is known as vapour pressure.
Diffusivity
The ratio of the flux to corresponding concentration gradient. Unit is m2/sec.
37. Difference : H2SO4 vs HNO3
H2SO4
H2SO4 is contain 2H+ ion. When H2SO4 dissolve in water it’s give 2H+ ion due to the ionization it’s get acidic.
38. Which gas was leak in Bhopal? Chemical structure of gas.
The name of gas methyl isocyanate (MIC)
H3C-N=C=O
39. Difference between batch process & continuous process
2. The orifice meter has a large permanent loss of pressure because of the presence of eddies on the downstream side of the orifice plate; the shape of the venturi meter prevents the formation of these eddies and greatly reduces the permanent loss.
3. The orifice is cheap and easy to install. The venturi meter is expensive, as it must be carefully proportioned and fabricated. Homemade orifice is often entirely satisfactory, whereas a venturi meter is practically always purchased from an instrument dealer.
4. On the other hand, the head lost in the orifice for the same conditions as in the venturi is many times greater.
5. However, in spite of considerations of power loss, orifices are widely used, partly because of their greater flexibility, because installing a new orifice plate with a different opening is a simpler mater.
6. It should be noted that for a given pipe diameter and a given diameter of orifice opening or venturi throat, the reading of the venturimeter for a given velocity is to the reading of the orifice as (0.61/0.98)2, or 1:2.58.(i.e. orifice meter will show higher manometer reading for a given velocity than venturi meter).
Batch process | Continuous process |
Concentration of Feed is decreasing with time | Concentration of Feed is remain constant with time |
Feed will not continuously charge. | Feed is continuously charge |
Labor requirement is more. | From one side and come out |
Time must be require. | From other side. |
Generally used for small scale production. | Time is not requiring. |
Manually operate. | Labor requirement comparatively less Automatically operate. |
40. What is the difference between evaporation and boiling?
Evaporation happens at any temperature whereas boiling occurs only at a single temperature for a single component like water. For example the water at sea surface evaporates everyday.
It may happen either at 300C or 350C, whereas water boils only at 1000C when the vapor pressure becomes equal to atmospheric pressure.
41. What is the difference between vapor and gas?
A vapor is formed by heating any liquid and it can be condensed at atmospheric conditions either by reducing temperature or be increasing pressure.
But a gas has already above the critical temperature and can’t be condensed by application of above methods. First it has to be brought below critical temperature. Then only it can be condensed.
42. What is wax? What is salt? What is osmosis process?
• Wax is form of liquid substance. it is made from long chain hydrocarbon compound.
• Salt is chemical compound which is obtained by neutralization of acidic and basic substance.
• The process by which solvent molecules of solution move from higher concentration to lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.it is called osmosis
43. What is shear stress and shear strain?
Shear stress
shear stress is stress (external force) acting on an object or surface parallel to the slope or plane.τ = F/A
F= force applied
A= cross sectional area of material
Deformation of solid due to stress.ε = di/Io
di = change of length
Io = initial length
shear stress is stress (external force) acting on an object or surface parallel to the slope or plane.
τ = F/A
A= cross sectional area of material
Deformation of solid due to stress.
ε = di/Io
Io = initial length
44. What is corrosion inhibitor?
45. What is difference between mild steel and stainless steel?
The most basic difference between mild steel and stain less steel is in their composition.- Mild Steel is made from a combination iron and carbon. It is most suitable in the construction industry and for making heavy equipment.
- Stainless steel made from a combination of chromium and iron. The resulting metal is noncorrosive and resistant to rusting.
46. Define Exothermic & Endothermic reaction.- Exothermic reaction: - a reaction which release the heat energy.
- Endothermic reaction: - a reaction which absorb the heat energy.
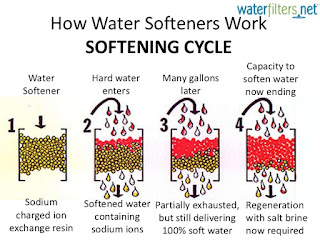
47. How hard water can be softened?- by zeolite process
- ion exchanger requires
- lime softening
- reverse osmosis
- on boiling
48. What is cloud point & pure point?
Cloud point
Cloud point refers to the temperature below which wax in diesel or biowax in biodiesels form a cloudy appearance.
Pour point
The pour point of a liquid is the temperature at which it becomes semi solid and loses its flow characteristics.
Cloud point refers to the temperature below which wax in diesel or biowax in biodiesels form a cloudy appearance.
The pour point of a liquid is the temperature at which it becomes semi solid and loses its flow characteristics.
49. Define elementary reaction & non-elementary reaction.
Elementary reaction
It is chemical reaction in which one or more chemical species react directly to form of products in single step & with single transition state.
Non-elementary reaction
A reaction that can be broken down into a number of steps. the rate of reaction will be determined only by the reactants involved in the slowest steps.
Non-elementary reaction
A reaction that can be broken down into a number of steps. the rate of reaction will be determined only by the reactants involved in the slowest steps.
50. Define leaf filter and plate filter.
Leaf filter
- These filters provide large surface area by using varieties of filter leaves and do not require complete disassembly for cleaning that is necessary with plate end frame filter press.
- The filter leaf in general consist of a heavy wire drainage screen mounted in a tubular frame which acts as support and filtrate conduit. The slurry to be filtered fills the space around the leaf by applying pressure on the slurry or vacuum within the leaf.
- In either case the filter cake builds upon the outside of leaf and filtrate passes from within the leaf to the filtrate discharge system.
Plate filter
- Slurry to be filtered is pumped through the feed channel. If runs into the chamber and fills the chamber completely the pressure goes on increase.
- The solid are deposited on the filter cloth. The two cake is formed simultaneously in chamber.
- The press is then dismantled and the cake of solid scrapped off from each plate and dropped to a conveyor or strange bin.
- Than it is washing simply and discharge the filtrate.
- These filters provide large surface area by using varieties of filter leaves and do not require complete disassembly for cleaning that is necessary with plate end frame filter press.
- The filter leaf in general consist of a heavy wire drainage screen mounted in a tubular frame which acts as support and filtrate conduit. The slurry to be filtered fills the space around the leaf by applying pressure on the slurry or vacuum within the leaf.
- In either case the filter cake builds upon the outside of leaf and filtrate passes from within the leaf to the filtrate discharge system.
- Slurry to be filtered is pumped through the feed channel. If runs into the chamber and fills the chamber completely the pressure goes on increase.
- The solid are deposited on the filter cloth. The two cake is formed simultaneously in chamber.
- The press is then dismantled and the cake of solid scrapped off from each plate and dropped to a conveyor or strange bin.
- Than it is washing simply and discharge the filtrate.
51. Name any four type of pipe fitting & it’s application.
52. What is the function of Manometer?
53. What are inert gases? Why they are inert? Give the names of 4 inert gases.
- An inert gas is a gas which does not undergo chemical reactions under a set of given conditions.
- Inert gases are generally used to avoid unwanted chemical reactions degrading the sample. These undesirable chemical reactions are often oxidation & hydrolysis with oxygen and moisture in air.
- Examples
- Purified ARGON
- NITROGEN
- NEON
- HELIUM
- CO2.
- Purified ARGON
- NITROGEN
- NEON
- HELIUM
- CO2.
54. Define : Corrosion and erosion
Corrosion
It is natural process in which degraded the useful property of material such as strength, structure. It occurs in metal but sometimes in polymer.
Erosion
It is action of surface process that removes soil, rocks or dissolves material from the one location to another.
55. Define : Saponification
When an oil or fat is boiled with a solution of caustic soda, the resultant product are soap and glycerin. The chemical reaction is called saponification.
Oil + NaOH -------- > Soap + Glycerin
56. Give difference between aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Aromatic Compound | Aliphatic Compound |
They are containing aromatic ring or benzene ring. | They are organic chemical compound without benzene ring. |
They are always cyclic. | They are linear and cyclic. |
They are always unsaturated. | They are saturated and unsaturated. |
They are conjugated due to the presence of alternating double bond. | The majority of aliphatic compound are not conjugated. |
57. Write difference between Forward feed and Backward feed evaporation.
Forward Feed Evaporator | Backward Feed evaporator |
-It’s not required pump. | -It’s required pump. |
-In this process heating of feed in first effect. | -In this process heating of feed in each effect. |
-Maintenance cost and power cost is less. | -Maintenance charge and power cost is high. |
-Get less thick liquor. | -Get thick liquor. |
58. Write difference between single effect and multiple effect evaporator.
- In multiple effect evaporator vapour coming out from 1st evaporator is use as feed for 2nd While in single effect evaporator vapour coming out from evaporator is going to condenser and discard.
- Cost of multiple effect evaporator is higher than single effect
- Multiple effect evaporator is use in large scale
 |
| Single effect evaporator |
 |
| Multiple effect evaporator |
Spray Dryer
60. Difference between drying and evaporation.
DRYING EVAPORATION -Small amount of solvent removed. -Large amount of solvent removed. -Remove solvent below boiling point. -Remove solvent at boiling point. -Main purpose to get dried product -Main purpose to increasing concentration of product.
61. Write driving force in Mass transfer operation, Heat transfer operation, Momentum transfer operation.- Mass transfer operation: – Transfer of mass from higher concentration to lower
- Heat transfer operation: – Transfer of heat from higher temperature to lower
- Momentum transfer operation: – Transfer of fluid from higher velocity to lower
- Momentum – Mass × Velocity
DRYING | EVAPORATION |
-Small amount of solvent removed. | -Large amount of solvent removed. |
-Remove solvent below boiling point. | -Remove solvent at boiling point. |
-Main purpose to get dried product | -Main purpose to increasing concentration of product. |
61. Write driving force in Mass transfer operation, Heat transfer operation, Momentum transfer operation.
- Mass transfer operation: – Transfer of mass from higher concentration to lower
- Heat transfer operation: – Transfer of heat from higher temperature to lower
- Momentum transfer operation: – Transfer of fluid from higher velocity to lower
- Momentum – Mass × Velocity
62. Define Enthalpy.
Enthalpy is defined as thermodynamic state function denoted by letter “H”, that consists of internal energy system (U) plus product Pressure (P) & Volume(V) of the system.
H = U + pV
Unit - Joule, Calories
H = U + pV
Unit - Joule, Calories
63. What is difference between Bubble point & Boiling Point? What is difference between Dew point and freezing point?
Bubble point : It is temperature at which first bubble of liquid is formed.
Boiling Point : It is a temperature of liquid at which vapour pressure of liquid is equal to atmospheric pressure [1 atm, 1.03323 Kg/cm²].
Explanation:
We have 2 chemicals mixture.
1. Less volatile chemical2. High Volatile chemicalVolatility of fluid : Capability of liquid to convert into vaporize.
When initial phase of boiling starts less volatile chemical starts to vaporize.At last high volatile chemical starts vaporizing.
Dew point : When any chemicals temperature is dropping, Whole vapour phase starts converting to liquid phase. At certain temperature there will no traces of chemical in vapour phase. This is dew point of Chemical.
Freezing point: When any liquid is converted into solid phase at 1 Atmospheric pressure. This temperature is Freezing point of fluid.
Volatility of fluid : Capability of liquid to convert into vaporize.
64. What is Avogadro number? What is its importance?
Numbers of molecules present in 1 mole.
Value : 6.023 * 10²³ / mole
65. What is Pressure test?
Pressure test is carried When any new Piping system or Pressure vessel is installed
For Piping system it should be capable to hold double pressure then maximum operating pressure for certain time.
For vessels and reactors it should be handle up to 1.5 times of maximum pressure for certain temperature.
If piping system is designed to 10 kg/cm² then pressure test should be carried to 20 kg/cm² [Some times this is carried on 15 kg/cm² it not recommended]
Reactor and vessel designed to 10 kg/cm² then pressure test should be carried to 15 kg/cm²
66. Which gas occupied maximum percentage in air?
Nitrogen- 78%
Oxygen- 21% Other gases-1%
Oxygen- 21%
67. Which catalysts are used in Chlorination and Hydrogenation?
AlCl3, FeCl3 and ZnCl2 is used in Chlorination
Pt, Fe and raney Ni is used in Hydrogenation
68.Define - Specific Heat. Latent heat and sensible heat
Specific Heat: The amount of heat required for rise one degree temperature per unit mass.
Latent Heat Is energy absorption or release by substance during phase change at same temperature.
Latent heat of Fusion: When energy exchange during Melting Solid of Freezing liquid.
Latent heat of Vaporization: When energy exchange during Vaporization of liquid
Latent heat of Condensation: When energy exchange during Condensate of vapour
Sensible Heat: is heat transfer of system till phase change.
Latent Heat Is energy absorption or release by substance during phase change at same temperature.
Latent heat of Fusion: When energy exchange during Melting Solid of Freezing liquid.
Latent heat of Vaporization: When energy exchange during Vaporization of liquid
Latent heat of Condensation: When energy exchange during Condensate of vapour
Sensible Heat: is heat transfer of system till phase change.
69. What is Ton of refrigeration?
Ton of refrigeration (TR)
Cooling capacity of an air conditioner or refrigerator equal to 12,000 British thermal units (Btu) per hour 200 Btu per minute and denotes the amount of heat required to melt one ton of ice in 24 hours.
1 TR = 12,000 Btu/hr
Cooling capacity of an air conditioner or refrigerator equal to 12,000 British thermal units (Btu) per hour 200 Btu per minute and denotes the amount of heat required to melt one ton of ice in 24 hours.
1 TR = 12,000 Btu/hr
70. Pressure drop equation for horizontal pipe line in laminar flow condition?
In fluid dynamics, the Hagen–Poiseuille equation is a physical law that gives the pressure drop in a fluid flowing through a long cylindrical pipe.
The assumptions of the equation are that the flow is laminar viscous and incompressible and the flow is through a constant circular cross-section that is substantially longer than its diameter.
71.Define Potential flow,Ideal fluid, definition
Ideal fluid is incompressible and it is having zero viscosity. Flow of Ideal fluid is known as potential flow.
Potential flow is highly developed flow.
Main characteristics of potential flow are
No eddies, no circulations within the fluid flow. So potential flow is irrotational flow.
No friction is developed in the fluid. Therefore there is no dissipation of mechanical energy into heat.
Therefore: Potential flow is incompressible, irrotational, highly developed and having zero viscosity.
No eddies, no circulations within the fluid flow. So potential flow is irrotational flow.
No friction is developed in the fluid. Therefore there is no dissipation of mechanical energy into heat.
Therefore: Potential flow is incompressible, irrotational, highly developed and having zero viscosity.
72. Pressure drop equation for horizontal pipe line in laminar flow condition?
In fluid dynamics, the Hagen–Poiseuille equation is a physical law that gives the pressure drop in a fluid flowing through a long cylindrical pipe.
The assumptions of the equation are that the flow is laminar viscous and incompressible and the flow is through a constant circular cross-section that is substantially longer than its diameter.
73. What is application of atomizer in Spray dryer?
Atomizer converts liquid in tiny droplets.
74. What are the units of Dynamic Viscosity?
75. What is Elutriation ?
Elutriation: It is a separation method, which depends on the settling velocity of the particles in the fluid.
In this process of separation, the material is placed in a rising fluid having a fixed upward velocity, particles whose normal falling velocity is less than the velocity of the fluid will be carried upward and out of the vessel.
If fractions obtained from a series of fluid velocities are collected and weighed, a complete size analysis may be obtained.
In this process of separation, the material is placed in a rising fluid having a fixed upward velocity, particles whose normal falling velocity is less than the velocity of the fluid will be carried upward and out of the vessel.
76. What is jigging and where it is used ?
Jigging:
Jigging is a separation method in which the particle are separated by using the density difference between them.
Jigging is a method of gravitational preparation of natural resources, based on separation of mineral mixture on density in vertically oscillating water stream.
Usually it is used to separate metal slag form metals.
Jigging is a separation method in which the particle are separated by using the density difference between them.
Jigging is a method of gravitational preparation of natural resources, based on separation of mineral mixture on density in vertically oscillating water stream.
Usually it is used to separate metal slag form metals.
77. What is Intensive and Extensive properties?
Intensive property:
It is defined as one which doesn't depends on the quantity of matter present in the system.
Examples: Temperature, pressure,Molar enthalpy, molar volume
Extensive property:
Is defined as one which depends on quantity of matter specified in the system.
Examples: Total mass, volume, Energy, enthalpy,
It is defined as one which doesn't depends on the quantity of matter present in the system.
Examples:
Extensive property:
Examples:
78. What are differences between pipe and tube?
Pipes and tubes are specified in terms of their diameter and wall thickness.
Pipes:
Heavy walled
Relatively large in diameter
comes in moderate lengths (20 to 40 ft)
Threading is possible
Pipe walls are rough
Lengths of pipes are joined by screwed, flanged and welded fittings
Made by welding , casting, or piercing a billet in a piercing mill
The wall thickness of the pipe is indicated using schedule number
Size of the pipe is indicated as nominal diameter
Tubes:
Thin walled
Less diameter
available in the form of coils also, several hundred meters
Can not be threaded
Tube walls are smooth
These are joined by compression fittings, flare fittings, or soldered fittings
These can be cold drawn
Tube thickness is indicated using BWG (Birmingham wire gauge)
Size of the tube is indicated as outside diameter
Pipes:
Heavy walled
Relatively large in diameter
comes in moderate lengths (20 to 40 ft)
Threading is possible
Pipe walls are rough
Lengths of pipes are joined by screwed, flanged and welded fittings
Made by welding , casting, or piercing a billet in a piercing mill
The wall thickness of the pipe is indicated using schedule number
Size of the pipe is indicated as nominal diameter
Tubes:
Thin walled
Less diameter
available in the form of coils also, several hundred meters
Can not be threaded
Tube walls are smooth
These are joined by compression fittings, flare fittings, or soldered fittings
These can be cold drawn
Tube thickness is indicated using BWG (Birmingham wire gauge)
Size of the tube is indicated as outside diameter
79. What is liquid and its properties?
Liquid is defined as a material which will take the shape of the container. It is one of the three classical states of matter.
Examples:
water, ethanol, most of the organic solvents.
Properties:
Liquids tend to have better thermal conductivity than gases, and the ability to flow makes a liquid suitable for removing excess heat from mechanical components.
The heat can be removed by channelling the liquid through a heat exchanger, such as a radiator, or the heat can be removed with the liquid during evaporation
Liquid is the primary component of hydraulic systems, which take advantage of Pascal's law to provide fluid power.
Devices such as pumps and waterwheels have been used to change liquid motion into mechanical work since ancient times.
Oils are forced through hydraulic pumps, which transmit this force to hydraulic cylinders. Hydraulics can be found in many applications, such as automotive brakes and transmissions, heavy equipment, and air-plane control systems.
Various hydraulic presses are used extensively in repair and manufacturing, for lifting, pressing, clamping and forming
Mechanical properties:
Volume: Commonly liquids are measured in the units of volume. SI units for volume are m3.
Pressure:
Hydrostatic head is the main property of the liquid. This hydrostatic head is calculated as P= h*rho*g. h = height of the liquid column, rho = density of the liquid, g = acceleration due to gravity.
Examples:
Properties:
Liquids tend to have better thermal conductivity than gases, and the ability to flow makes a liquid suitable for removing excess heat from mechanical components.
Liquid is the primary component of hydraulic systems, which take advantage of Pascal's law to provide fluid power.
Mechanical properties:
Volume: Commonly liquids are measured in the units of volume. SI units for volume are m3.
Pressure:
Hydrostatic head is the main property of the liquid. This hydrostatic head is calculated as P= h*rho*g. h = height of the liquid column, rho = density of the liquid, g = acceleration due to gravity.
80. Convert 1 atm pressure terms to other units?
1 atm pressure
= 760 torr= 760 mmHg= 101.325 kPa=101.325 kN/m2= 1.103 bar= 1.103 kg/cm2= 14.7 psi ( pressure per square inches)
81. What is chemistry?
Chemistry is the study of the composition of matter.
82. What is a chemical change?
A change, in which a new substance with different properties is formed, is known as chemical change.
83. Give example of physical change?
Dissolving sugar in water
84. What are the forms in which matter exists?
Elements Compounds and Mixture of elements and compounds.
85. What is element?
Elements are the organic materials from which all substances like solid, liquid and gas is made. It is the simplest form of matter.
86. What are the more abundant elements in the earth's crust?
O2 49.6%
Sodium 2.6%
Silicon 25.8
Aluminum 22.0
87. What are the major elements in the Human body?
Oxygen 65%
Carbon 18%
Hydrogen 10%
Nitrogen 3%
Calcium 2.4%
Phosphorus 1.0%
88. What is a compound?
Compounds are pure substances formed from the chemical reaction of elements. They have same composition and same properties, cannot be broken down except by chemical reactions.
89. What is an atom? What is it made up of?
Atoms are smallest particles of elements which can exist with the properties of the element. Different atoms of the same elements are alike in always, atoms of different elements are unlike.
It consists of a nucleolus composed of proton and neutrons with electrons around the nucleus, protons are positively charged, electrons are negatively charged and neutrons are neutral.
90. What is Atomic number ? What is Atomic weight?
Atomic number is the number of protons in the atom of an element, which is equal to the number of electrons.
Oxygen as a standard to the weight of the atoms of elements, which are too small to be measured or to mean any thing. Oxygen is given a number 16 as it is a atomic weight. Atomic weight of all other elements is relative to this figure.
91. What is Valancy? What is the valance of carbon atom?
Valancy is combining capacity of an atom. The number of electrons, gained, lost or shared by an atom is the valance. Carbon atom has a valance of four.
92. What is Radical?
A radical is a group of atoms different elements are linked together in chemical reactions. A radical behaves like a single atom.
93. What is a molecule?
Molecules are the smallest parts of compounds, some elements like Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, etc., exist as molecules of two atoms.
H2, N2, O2
94. What is organic compound?
Organic compounds are obtained directly or indirectly from living organisms,. Since carbon compounds are the most important compounds of plants and animals, organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbons compounds.
95. What is inorganic compound?
Inorganic means 'no life' and inorganic chemistry concerns itself with the elements and compounds other than those of carbon.
96. What is Crude oil composed of?
Crude oil is mainly a mixture of hydrocarbon compounds of carbon and hydrogen. It also contains relatively small quantities of sulfur, oxygen and nitrogen.
97. How many different types of crude are there in the world?
There are hundreds of different crude oils, perhaps even thousands. Some crude oils have lighter specific gravities than others, some have lower total sulfur content than others, some can be refined to produce more gasoline than others, and some have lower pour points than others.
The physical properties of any specific crude oil are obtained by a series of laboratory tests which result in what is called a "crude oil assay".
Some people classify crude oils as: paraffin base; naphthene base; aromatic base; asphalt base; or mixed base.
The general elementary composition of crude oil falls within these approximate weight percent ranges: Carbon = 80 to 87, Hydrogen = 11 to 14, Nitrogen = 0.2, and Sulfur = 0 to 3.
98. What is the basis of classifying hydrocarbon?
On the basis of Chemical structure.
99. What the major hydrocarbon families’ deal within refinery/petrochemical processing mainly?
- PNAO
- Paraffins,
- Naphthenes,
- Aromatics and
- Olefins.
(Of these all but Olefins are found in natural crude)
100 . How we are getting petro products? What are main fractionation products from Petroleum?
The manufacture of petroleum product is the separation of crude oil into the main fractions by distillation.
Fractionation products from Petroleum
- Gas
- Naphtha (benzene)
- Kerosene (paraffin)
- Diesel
- Lubricant
- Fuel oil
101. What is a chemical reaction?
It is a chemical change in which elements combine to form compounds or breaking out compounds to recombine to form new compounds.
102. What is exothermic reaction? What is Endothermic reaction?
A chemical reaction in which heat is liberated is called exothermic reaction
Example: union fining reaction
A chemical reaction in which heat is absorbed is call endothermic reaction
Example: pacol reaction
103. What is DPK? Where Return kerosene is used?
DPK: Duel purpose kerosene. Return kerosene used as Jet A, B, JP & JPB)
104. What is paraffin?
Carbon atoms connected in a straight chain by single bond (normal) Butane C-C-C-C
105. What are iso paraffins?
Carbon atoms having branched chain, single bond arrangement is called Iso-parafins (non-normals).
Iso-butane C- C - C
|
C
106. Why kerosene selected for Normal Paraffin production?
Normal paraffin is rich in kerosene carbon range, almost about 18.5% with C10-13 range. Average Molecular Weight of heart cut is about 165.
107. What are the characteristics of straight chain paraffins?
- Saturated compounds with a general formula CnH2n+2 Good natural stability.
- Natural high Viscosity Index (V.I) lubricating oils.
- Good source of waxes.
- Poor for manufacture of Gasoline.
- Hard carbon deposits.
- High pour point
- Found particularly in paraffin crude.
108. What changes in properties occur when paraffin are isomerizes?
- Boiling point is lowered.
- Octane number is increased.
109. What are the properties of Naphthenic hydrocarbons?
- They are cyclo paraffin
- They are saturated with a genera formula CnH2n+2
- Low VI
- Low pour point
- Better octane rating than corresponding paraffin.
- Naphthenic Motor oils form sort, fluffy carbon deposits.
110. What are the properties of olefins?
- They are unsaturated.
- Readily react with oxygen to form sludge.
- Possess good anti-knock properties.
111. What are the properties of Aromatics?
- They are not very reactive in spite of the presence of double bonds.
- They behave more like saturated compounds.
- Excellent anti-knock properties.
- Used as commercial solvents due to their high solvent power.
- Poor VI components.
- Produces smoky flames
112. What is cracking?
Heavier hydro carbons are cracked or broken into smaller molecules to produce more valuable lighter products from the low priced heavier hydrocarbons.
113. What is Alkylation?
It is the process of combing two dissimilar hydrocarbons. A catalyst is used in this reaction of saturated compounds with unsaturated.
114. What is Polymerization?
Similar to Alkylation, except that in this case two un saturates are combined over a catalyst.
115. What is Hydrogenation or Hydro finishing reaction?
In this reaction hydrogen combines with unsaturated hydrocarbon make them a saturated compound over a catalyst.
116. What is Hydro De-sulfurization?
A reaction over a catalyst to remove sulfur by converting it to H2S with addition of hydrogen.
117. What is the reaction involved in decoking of furnace & regeneration of catalyst?
It is Oxidation. Using oxygen from the air the coke is burnt to CO2.
118. What is temperature? What is freezing point? What is the freezing point of kerosene?
It is a measure of how hot something is.
The temperature at which crystals first appear when a liquid is cooled under specified conditions.
Kerosene freezing point -47oC.
119. What is Dew point?
The temp at which condensation of water vapor from the air begin the temp of the air water vapor mixture falls.
120. What is Dry bulb temperature? What is Wet bulb temperature?
It is an indication of the sensible heat content of air water vapor mixtures
It is measure of total heat content or enthalpy. It is the temperature approached by the dry bulb and the dew point as saturation occurs.
121. What is Dew point temperature?
It is a measure of the latent heat content of air-water vapor mixtures and since latent heat is a function of moisture content, the dew point temperature is determines by the moisture content.
122. Write difference between density and Specific gravity?
Fuel density: mass of the fuel to the volume at specified temperature.
Specific gravity of fuel: density of fuel, relative to water is called specific gravity. Higher the sp gravity, higher will the heating values.
123. What is Calorific value (CV)?
Energy content in an organic matter (CV) can be measured by burning it and measuring the heat released. The heating value of fuel is the measure of the heat released during the complete combustion of unit weight of fuel.
It is expressed as Gross Calorific Value (GCV) or Net Calorific Value (NCV).
124. What is the difference between GCV and NCV?
The difference between GCV and NCV is the heat of vaporization of the moisture and atomic hydrogen (conversion to water vapor) in the fuel.
Typical GCV and NCV for heavy fuel oil are 10500 kcal/kg and 9800 kcal/kg.
125. How does define a "barrel"? How many liters and Gallons in a US barrel of crude oil?
The "barrel" is a volumetric unit.
1 barrel is equivalent to 42 U.S. gallons or 34.97 Imperial gallons or
158.99 liters or 5.615 Cubic feet.
How many liters and Gallons in a US barrel of crude oil?
159 Liters, 42 Gallons
126. What is specific gravity?
Specific gravity is used to measure liquid density
127. What is the relation between Sp. Gravity and API gravity?
Heavier hydrocarbons will have higher specific gravity and low API gravity.
128. How do you calculate API Gravity?
129. How do you convert Sp. Gravity (0.8020) to API gravity?
130. How do you calculate Sp.gravity of a crude oil at a given API 45?
141.5/131.5 + 45 = 0.8017
131. Why do we treat lowers API gravity crude to meet product specification?
Lower API crude requires high temperature and longer retention time to meet proper oil product specification.
132. What is heat?
It is an energy associated with the motion of molecules in a substance.
133. What is the basic principle of heat transfer?
Heat transfer is the transfer of heat from hot place to cold place.
134. What is the effect of boiling point in relation with pressure?
Boiling point increases at high pressure and decreases at low pressure.
135. What happens to vapor pressure when it reaches to boiling point?
At boiling point vapor pressure of a liquid equalizes to the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere.
136. What is the purpose of a hazardous area classification drawing? Give examples of Zone 0, Zone 1 and Zone 2
Hazardous areas are classified as
- Zone 0 (Class 0)
- Zone 1 (Class 1)
- Zone 2 (Class 2)
Examples of Zone 0, Zone 1 and Zone 2
Zone 0 = Always air fuel mixture is continuously present.
Example: Tank vents, Sump vents, Drains etc.
Zone 1 = Air fuel mixture is present during normal operations.
Example: Pipe line flanges, Inlet manifold areas. (Flange joints are the weaker areas in a process system that may cause leak during abnormal Operation).
Zone 2 = Air fuel mixture is may present during abnormal operations.
Example: Welded pipelines where there are no flange joints. This area reduces the chances of leaks. Flare lines, welded hydrocarbon pipelines where there are no flanges.
137. What is a natural gas?
Natural gas is produced from organic compounds or hydrocarbons during the process of crude oil / gas production operations from an oil reservoir.
138. Why do we consider methane is the lightest gas?
Methane has only one carbon atom.
139. What is viscosity?
Viscosity is the resistance of a liquid to flow.
140. What is pressure? How do you calculate pressure of 100 pound block measuring 25 Square inches on each side?
Pressure is the measure of force applied to a unit area.
Pressure = Force/Area
100/25 = 4 psi.
141. Why do we use vacuum scale?
Vacuum scale is used to measure pressure in vessels which are below atmospheric (Absolute).
142. What reading on a mercury vacuum gauge corresponds with the Atmospheric pressure?
Zero in Vacuum gauge is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
143. What is a perfect vacuum?
Zero pressure absolute Psia equals the pressure in a perfect vacuum.
144. What is RTD?
RTD is resistance Temperature Detector. (Heat creates by Electrical Resistance). Increase the heat means increases the resistance.
145. What is the unit of electrical resistance?
Unit of electrical resistance is Ohms at 0 oC .
146. Expand the P&ID abbreviations?
- FSH Flow switch high,
- FR Flow recorder
- FRC Flow recorder Controller
- FIC Flow indicating Controller
- PR Pressure recorder
- PRV Pressure Relief Valve
- TSV Temperature safety valve
- ESD Emergency Shut Down
- PDIC Pressure differential indicating controller
- PCV Pressure control valve
- FCV Flow control valve
- TCV Temperature control valve
- LCV Level control valve
- PSHH Pressure switch high high
- FSHH Flow switch high high
- TSHH Temp. Switch high high
- PSLL Pressure switch low low
- LO Lock open
- LC Lock closed
- TIC Temperature indicating controller
- CSO Car Seal Open (valve sealed and kept in OPEN position)
- CSC Car Seal Closed (valve sealed and kept in CLOSED condition)
147. Find the following from P&ID?
- Pipe line specifications
- Fail open valves
- Fail closed valves
- Restricted orifice plates
- Lock open valve
- Lock closed valves
- Piping insulation
- Pneumatic inst. Signal lines
- Level controller
- Level relay switch
- Pressure control valves
- Reducers
- Shutdown valves
- Spectacle blinds
- Reciprocating pump
- Pulsation damper
148. What is a mixture? Give two examples.
Mixture is a composition of two or more molecules of an element that are not chemically bonded and can be physically separated.
149. What happens to the volume of gas from one stage to the next stage?
Volume reduces when compressed gas move out from one stage to the next stage.
150. At what temperature the movement of molecules completely stops?
At absolute zero temperature.
151. What is difference between deposition and sublimation?
What is difference between melting and freezing?
What is difference between vaporization and condescension?
Overall conversion
Solid into liquid called Melting.
Liquid into solid called freezing.
Liquid into gas called vaporization.
Gas into liquid called condensation.
Gas into solid called deposition.
Solid into gas called sublimation.
152. How much power required for agitation?
It is a function of RPM.
It is also depends on
- Viscosity of fluid
- Density of fluid.
- Dimensions of vessels and Impeller
It is related by dimensionless form as:
Where153. Difference between Absorption and Adsorption
In absorption, one substance (matter or energy) is taken into another substance. But in adsorption only the surface level interactions are taking place.
154. Difference between Liquid and Aqueous solution.
• Liquid is a state of matter, while aqueous is a special type of liquid formed by dissolving a compound in water
• All aqueous solutions are liquids, but not all liquids are aqueous solutions
155. State Laws of conservation of energy?
According to the laws of conservation of energy, “energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. It can only be transformed from one form to another.”
156. Define Reynolds number.
Reynolds number is the ratio of inertial force and viscous force. It is a dimensionless number. It determines the type of fluid flow.
157. What is a Newtonian fluid?
A Newtonian fluid possesses a linear stress strain relationship curve and it passes through the origin. The fluid properties of a Newtonian fluid do not change when any force acts upon it.
158. Difference between Strainer and Filter
Strainer for coarse size, Filter is more accurate than Strainer.
159. What are differences between Welding & Brazing?
In Welding concentrated heat (high temperature) is applied at the joint of metal and fuse together.
In Brazing involves significantly lower temperatures and does not entail the melting of base metals.
Instead, a filler metal is melted and forced to flow into the joint through capillary action.
160. What is the difference between Blower and Fan?
Fan is an air pushing device. Either Axial or Centrifugal type systems are used to move the air in low pressure. It is rotated by a motor separately.
When the fan is a housing of blades and motor, then it called as Blower. It directs the air in a single path with high pressure.
161. Is gate valve used for Throttling?
Gate valves are not suitable for throttling because the control of flow is difficult for the valve’s design, and the flow of fluid slapping against a partially open gate can cause extensive damage to the valve.
162. Why is the Suction pipe of Vapour Compression Refrigeration system insulated?
1. It prevents the suction line from sweating and dripping water inside the house.
2. The insulation also prevents the suction line attracting heat from the outdoors on its way to the condenser coil.
163. What is molecular sieve?
Answer: Molecular sieve means a solid micro porous alumina silicate with uniform pore geometry it is called as zeolite
165. What are the various graphical methods for the calculation of number of plates in distillation column?
There are three methods
- Mccabe thiele method
- Ponchon sevrit method
- Lewis sorel method
- Mccabe thiele method
- Ponchon sevrit method
- Lewis sorel method
166. What is normal tray spacing (Distance between two plates) in distillation column?
167. What are the different types of tray efficiencies?
Answer:
There are three types of tray efficiencies
- Local or point efficiencies
- Murphee plate efficiencies
- Overall efficiency
Overall plate efficiency = No of ideal trays required / No of actual trays required
There are three types of tray efficiencies
- Local or point efficiencies
- Murphee plate efficiencies
- Overall efficiency